No products in the cart.
Vietnamese hair
All about thickness of human hair you need to know
Let’s dive into the world of thickness of human hair and discover how to measure hair thickness with Jen Hair.
The thickness of human hair typically falls within the range of 0.016 to 0.05mm, and this dimension is influenced by your natural hair type. Dark hair tends to be thicker than blonde hair. There is no universal standard for hair thickness because each person’s hair thickness is determined by their unique genetic makeup. Understanding your hair’s thickness and how to measure it can help you know about the most suitable hair care practices.
What is the thickness of human hair?
Hair thickness, also known as hair diameter, pertains to the width of an individual hair strand. People often conflate the terms “hair thickness” and “hair density” due to their apparent similarity. However, in the context of human hair, these terms have distinct meanings.
Hair density relates to the total number of hair strands on a person’s scalp. It’s a measure of quantity rather than thickness, with a higher density equating to more voluminous hair. Thickness and density are interrelated factors that contribute to the appearance of fuller hair, as they work in tandem.
Much like the variation in hair densities, hair thickness can also exhibit a range of differences. Thickness refers to the width or diameter of an individual hair strand. It is essentially a quantification of how wide a single strand of hair is.
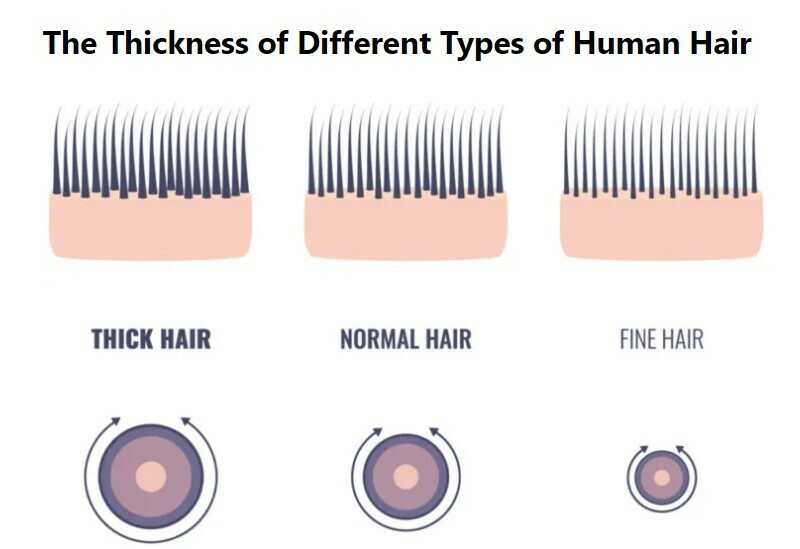
Average thickness of human hair
The diameter of a hair strand is typically measured with a specific measurement unit called micrometers (μm) or millimeters (mm), and it can range from extremely fine to coarse. Fine hair strands have a smaller diameter, typically falling within the lower end of the 0.016 to 0.05mm range, while coarse hair strands have a larger diameter. Average, a person’s hair ranges from 17- 181 µm.
In European standards, hair with a diameter ranging from 0.04 to 0.06 mm is generally categorized as thin, while hair with a diameter between 0.06 and 0.08 mm is considered normal, and hair measuring between 0.08 and 0.1 mm is labeled as thick. In comparison to European hair, Asian hair is notably thicker, with an average diameter falling in the range of 0.08 to 0.12 mm.
European hair tends to have a somewhat elliptical shape, whereas Asian hair is typically rounder and possesses greater elasticity. African hair, in terms of thickness, falls somewhere in between, though it doesn’t exhibit the same hair density as some other ethnic groups.
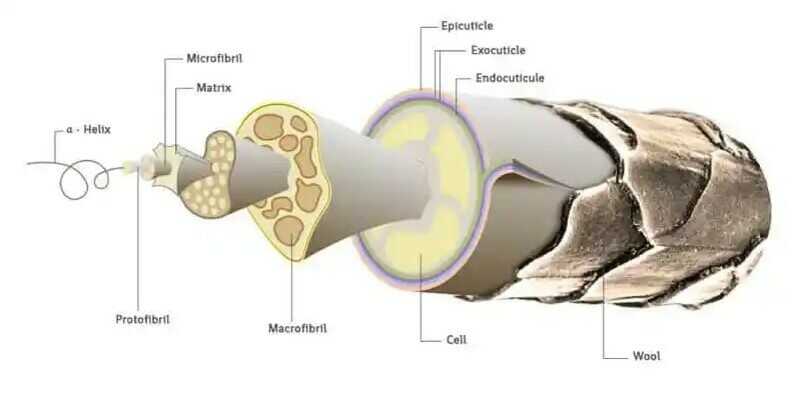
Human hair is primarily composed of approximately 80% keratin, serving as its primary constituent, and contains about 10-15% water. The remaining 5-10% is comprised mainly of pigments, minerals, and lipids. The hair body consists of 3 layers: the cuticle, the cortex, and the medulla.
How To Measure Hair Thickness?
Measuring the precise diameter of hair strands can be intricate, but there are practical methods to gauge whether your hair is fine, medium, or thick. While these techniques provide approximations, they are useful for estimation. A student measures the thickness of human hair by some methods:
Using Copy Paper
- Standard copy paper has a thickness of approximately 70 microns, which can serve as a reference for medium hair thickness.
- To assess your hair, compare it to this baseline. If your hair is roughly half as thick as the copy paper, it leans toward being fine. If it’s approximately twice as thick as the paper, it falls into the category of maximum thickness.
Sensory Evaluation
- If you suspect your hair is either fine or medium, try this tactile test.
- Take a strand from your hairbrush without plucking. Hold the strand between your fingers.
- If you can barely feel it, your hair is more likely to be fine. If you can sense a faint texture but it’s not coarse, it’s indicative of medium hair.
Comparison with Sewing Thread
- To confirm the suspicion of having thick hair, pluck a strand from a thicker-growing area.
- Obtain a piece of sewing thread and hold it up against the hair strand’s end for comparison.
- If the hair’s diameter is nearly as wide as the sewing thread, it aligns with the category of thick hair.
These methods provide a practical way to estimate your hair’s thickness without requiring complex measurements.

Factors contributing to hair thickness disorders
A multitude of factors can contribute to hair thinning, encompassing both lifestyle choices and underlying health conditions. Here are some prominent causes of decreased hair thickness:
Excessive Hair Treatments
Overuse of color treatments, hair gels, perms, and similar products can weaken the hair, leading to a reduction in its thickness. It’s important to choose products that are suitable for your hair type to protect its integrity. One natural and effective method to fortify your hair involves regular oiling, as it enhances blood circulation to the scalp, nourishes the follicles, and promotes hair strength. Hydration of the hair also enhances the chemical bonding between its various layers.
Lifestyle Habits
Sporting tightly pulled hairstyles for buns can increase the risk of hair thinning. This condition results from excessive strain on the hair. It’s essential to exercise caution during physical activities to safeguard the health of your hair. Daily habits can have a significant impact on the condition of your hair.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Deficiencies in essential nutrients like iron and folic acid can impact the thickness of human hair. Research has shown that iron deficiency can lead to hair thinning and eventual hair loss. Incorporating oral supplements in your diet can help address this issue. Other mineral deficiencies, including zinc, selenium, and biotin, can also influence hair thickness.
Hair Disorders
Conditions like pattern baldness are often associated with hair thinning. Studies have revealed a connection between diffuse androgenetic alopecia (female pattern hair loss) and decreased hair thickness. Hormonal imbalances can cause hair to become smaller in size, resulting in weakness. Alopecia areata (AA) is a significant hair disorder affecting millions globally, making hair thinner and more prone to breakage.
Stress effect to the thickness of hair
Psychological stress is a notable trigger for hair thinning. Non-scarring hair loss can occur as a consequence of emotional stress, often brought on by trauma, surgery, or severe infections.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can I measure the thickness of human hair in inches?
Many individuals seek to determine the thickness of human hair in inches or centimeters, although the standard unit for measuring hair strand thickness is micrometers (μm). To provide some perspective, there are approximately 25,400 micrometers in one inch, and 1 μm is equivalent to 0.0001 cm.
What factors affect the thickness of hair?
The color of the hair can impact its thickness, with darker hair generally being thicker than lighter hair. Darke hair is thicker than blonde hair because it has a middle layer.
How can I naturally make my hair thicker?
Your genes do not decide what your hair looks forever. You can thicken your hair in several ways such as: Hydrating your hair, trimming regularly, using some sulfate-free product,… to make your hair grow faster and thicker.
Is men’s hair thicker than women’s hair?
It is a common perception that men’s hair is often thicker than women’s hair, but this is not universally true. Some men may have very fine and thin hair, while some women may have thick and coarse hair. Additionally, hormonal changes and aging can affect the thickness of hair in both men and women.
Conclusion
As demonstrated in the information provided above, various factors influence hair thickness. In this article, Jen Hair aims to guide you on measuring hair thickness and understanding the factors that impact it. This knowledge will enhance your understanding of your hair and how to care for it effectively.
 Top 10+ breathtaking dreadlock styles for weddings
Top 10+ breathtaking dreadlock styles for weddings How to add volume to hair men: 7 useful tips
How to add volume to hair men: 7 useful tips 18 inch wig chart: An ultimate length chart and measurement guide
18 inch wig chart: An ultimate length chart and measurement guide
