No products in the cart.
Hair Care Guide
Discover Hair Textures Chart And Understand Your Hair Types
Let’s understand about different hair types through a hair textures chart, as well as finding appropriate methods to maintain your hair strong and bright.
In general, there are four main hair types, including straight, wavy, curly, and kinky or coiled. Then, each category has three subcategories with different curl patterns and thicknesses.
Because of their different hair textures, what works for one hair type might not be suitable for another. By understanding these differences, you are more likely to find the best ways to style and maintain your hair.
Below you will find a hair textures chart that will give you insights into your specific hair type. In the end, you will acquire comprehensive knowledge about different hair types and appropriate methods to maintain strong and bright hair.

What is Hair Texture?
The texture of your hair depends on how thin or thick each individual hair strand is. There are three main categories for hair texture – fine, medium, and thick.
- Fine hair has very skinny and delicate strands. This type of hair lacks volume and body. The thin strands get knotted and snap easily. It’s challenging to keep hairstyles looking neat with fine hair because the strands don’t hold the style well. Fine hair also tends to look oily or greasy quickly after washing it. Using a lot of hair products like gels or sprays weighs down fine hair and causes more strands to break off.
- Medium hair has strands that are thicker and stronger than fine hair. Like fine hair, it has an outer and inner layer. But medium hair may also have a third, inner layer called the medulla. Medium hair doesn’t break as easily as fine hair and hairstyles last better.
- Hair that is thick and rough has the thickest strands. These strands are resistant to damage. Thick hair has three layers – an outer layer, a middle section, and an inner core. Because it is so full and thick, this type of hair can hold hairstyles in place well. However, thick hair takes a long time to fully dry after getting wet. It can also become frizzy and puff out when the weather is humid and there is a lot of moisture in the air.
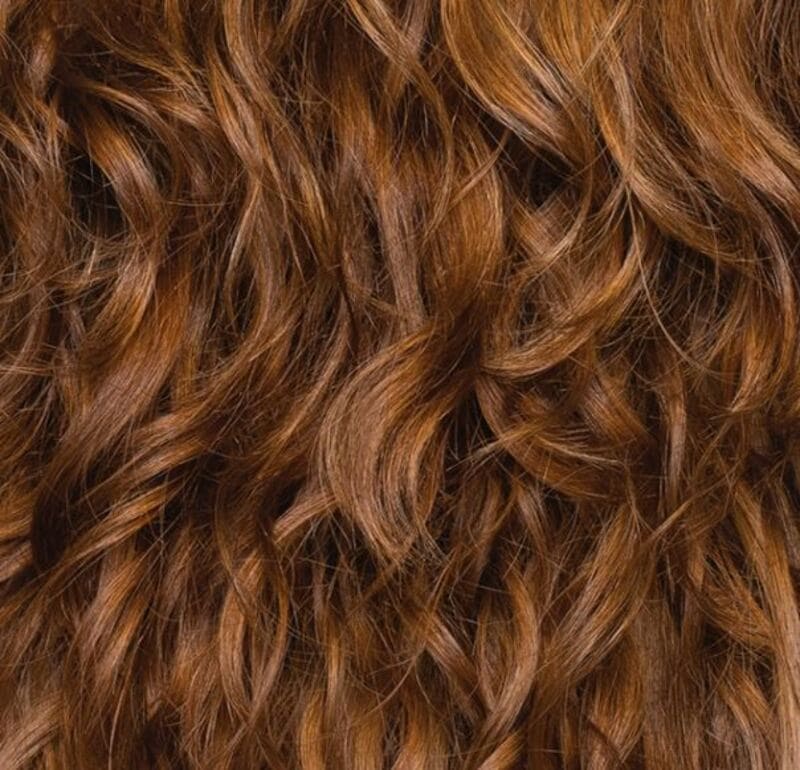

All Hair Textures Chart
Hair type is about whether your hair is naturally straight, wavy, curly, or very curly. Your hair type shows if you have straight hair, hair with some waves, hair with lots of curls, or hair with tight coils. In addition, your hair texture tells you if you have fine, thin strands or thick, coarse strands.
Understanding the different hair types can be a bit tricky because there are subcategories within each type. To make it easier to see the differences between the various hair textures, you can check out a hair textures chart.
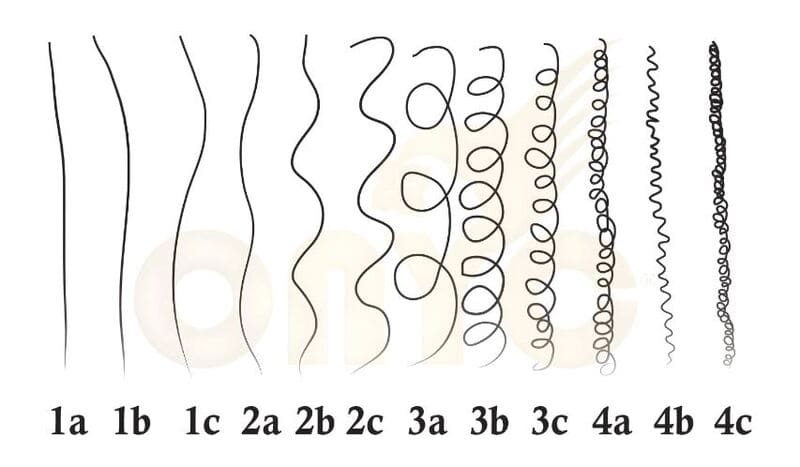
Straight Hair (Type 1)
Straight hair is usually fine and can get oily and shiny quickly because the natural oils from the scalp travel down the hair shaft easily without curls to slow them down.
- Type 1A hair is very straight and fine, commonly found among Asian people.
- Type 1B hair is thicker than 1A, still straight, but has a bit more volume.
- Type 1C hair is very thick and coarse, yet still straight and shiny, which can make it challenging to hold curls.
Wavy Hair (Type 2)
This type has more curl than straight hair but less than other types. It is typically thicker than Type 1.
- Type 2A hair is wavy and can be fine or a bit coarser. It has gentle S-shaped waves and is easy to style.
- Type 2B hair is wavy and medium-thick, but it may be prone to frizz.
- Type 2C hair is wavy, thick, and coarse. It tends to get frizzy and can be difficult to style.
Curly Hair (Type 3)
These curls straighten when wet and bounce back as they dry. It is relatively easy to style and has defined springy curls.
- Type 3A hair is shiny and thick, with well-defined curls. It may experience frizz.
- Type 3B hair has tighter curls and can have a mix of different textures.
- Type 3C hair is more closely coiled, pencil-sized curls.
Coily Hair (Type 4)
This hair type is often coarse and delicate, prone to damage. Healthy Type 4 hair will have shine and elasticity.
- Type 4A hair has soft, tight, and well-defined curls.
- Type 4B hair is also soft but more fragile, with tighter and less defined curls.
- Type 4C hair has extremely tight curls that may not appear curly at first glance.
Can You Change Your Hair Texture?
Your hair texture can potentially change, although it’s not very common. Following are several factors can contribute to changes in hair texture:
- Age: As we get older, our hair may become thicker or thinner, affecting its texture.
- Hormones: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy or menopause can impact how your hair feels and looks.
- Health issues: Certain medical conditions like not having enough iron in your blood or a thyroid problem can sometimes lead to changes in your hair’s texture, making it feel coarser or finer.
- Using hot styling tools: If you frequently use things like flat irons, curling irons, or blow dryers on high heat settings, it can damage and alter the texture of your hair strands over years of use.
- Chemical treatments: Hair dyes, relaxers, and perms that contain chemicals can also alter the natural texture of your hair.
Remember, while changes in hair texture can happen, they aren’t as common as changes in hair thickness or color.

If you’re looking to alter your hair texture, here are some options to consider:
- Heat styling: Utilizing heat styling tools like flat irons or curling irons can temporarily transform your hair’s texture.
- Chemical treatments: Relaxers and perms are chemical options that can permanently change your hair texture, but they can also cause damage.
- Hair extensions: Adding hair extensions can create the illusion of thicker or longer hair while also introducing texture.
- Haircuts: Opting for specific haircuts, such as layers or texturizing techniques, can enhance the texture of your hair.
- Products: Using products like sea salt spray or texturizing sprays can provide additional texture to your hair.
Learn about Hair Porosity
Understanding hair types goes beyond texture – porosity is also important. Porosity measures how well your hair absorbs and keeps moisture. There are three levels: low, medium, and high.
Low porosity hair has tight cuticles, making it hard for moisture to get in. High porosity hair has gaps in its surface, so it soaks up moisture easily but struggles to keep it. This type of hair can also get frizzy in humid conditions.
Not sure about your hair’s porosity? Try the float test. Put a few hair strands in warm water and wait a bit. If they float, you likely have low porosity hair. If they sink, your hair probably has high porosity.

Low Porosity
Low porosity hair has trouble taking in moisture because its outer layer is very tightly closed. You can check if you have this type of hair by doing an easy test: put a hair strand in water. If it floats, you likely have low porosity hair. Another clue is if your hair takes a long time to dry after it gets wet. This happens because the hair has a hard time both letting water in and letting it out.
Medium to Normal Porosity
During the float test, if your hair doesn’t float on the water’s surface but still remains buoyant, it suggests that you likely have medium to normal porosity. This indicates that your hair’s absorption level is between low and high porosity. Having medium to normal porosity is considered ideal because it allows moisture to penetrate the hair easily while also enabling effective moisture retention.
High Porosity
Hair with high porosity has gaps and holes that allow it to absorb moisture rapidly. When conducting the float test, you will observe that your hair strands sink to the bottom of the bowl quickly. This characteristic of high porosity hair has both positive and negative aspects.
On the downside, highly porous hair is prone to frizz and dryness. It can be challenging to manage, easily gets tangled, and is susceptible to breakage. In humid climates, the hair tends to absorb moisture from the air, exacerbating these issues.
However, high porosity hair has the advantage of effectively absorbing products like moisturizers, which can nourish and strengthen the hair strands.

FAQs
What is the rarest hair texture?
There is no commonly agreed-upon “rarest” hair texture as it can vary based on geographical and ethnic factors. However, hair textures that are less common in certain regions or populations, such as extremely tight curls or certain types of wavy or straight hair, are considered rarer.
How can I tell what hair texture I have?
Hair texture is typically classified into categories based on curl pattern, thickness, and coarseness. You can determine your hair texture by observing your natural curl pattern, examining the thickness and diameter of your individual strands, and considering the overall appearance and behavior of your hair. Consulting with a hairstylist or hair care professional can also provide helpful insights.
What are the 12 different hair types?
The classification system for hair types commonly refers to four main categories (Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, and Type 4) with subcategories. However, the subcategories vary depending on the classification system used. For example:
- Type 1: Straight hair (subcategories: 1A, 1B, 1C)
- Type 2: Wavy hair (subcategories: 2A, 2B, 2C)
- Type 3: Curly hair (subcategories: 3A, 3B, 3C)
- Type 4: Coily/kinky hair (subcategories: 4A, 4B, 4C)
What is the most desired hair texture?
The perception of the most desired hair texture can vary greatly depending on cultural, societal, and personal preferences. Beauty standards and trends often influence people’s perceptions of desirable hair textures. It’s essential to embrace and appreciate the natural texture of your hair, regardless of societal preferences, as all hair types are beautiful and unique in their own way.

Final Thoughts
Understanding your hair texture is crucial for proper hair care and styling. By familiarizing yourself with the hair textures chart and identifying your specific hair type, you can better tailor your hair care routine to meet its unique needs.
In addition, whether you have straight, wavy, curly, or coily hair, embracing and caring for your natural texture is key to maintaining healthy and beautiful locks. If you’re interested in exploring hair extensions to enhance your hair’s length or texture, don’t hesitate to contact Jen Hair today!
Recommendations:
 Guide Cornrows With Side Part The Best For Beginner
Guide Cornrows With Side Part The Best For Beginner Ultimate Guide: Headband with Hair Attached (Best Styles for 2025)
Ultimate Guide: Headband with Hair Attached (Best Styles for 2025) Human Hair Clip In Extensions For Black Hair For Thin Hair
Human Hair Clip In Extensions For Black Hair For Thin Hair
